What is orthognathic surgery?
Orthognathic surgery, also known as corrective jaw surgery, is a procedure that can be done in combination with braces treatment to treat patients with bite problems arising from mismatched upper and lower jaw sizes or jaw asymmetry. Orthognathic surgery is done under general anaesthesia and typically requires hospitalisation of 2-5 days.
Examples of problems that may be addressed by jaw surgery include:
- Gummy smiles
- Flat mid-face
- Long lower jaw
- Short lower jaw or small chin
- Long face
- Open bite
- Facial asymmetry
Treatment planning is usually undertaken jointly by the orthodontist and an oral surgeon.
Who needs orthognathic surgery and why is surgery required?
Adult, non-growing patients with mismatched upper and lower jaw sizes may present with bite problems and be told that braces treatment alone cannot provide a satisfactory treatment outcome.
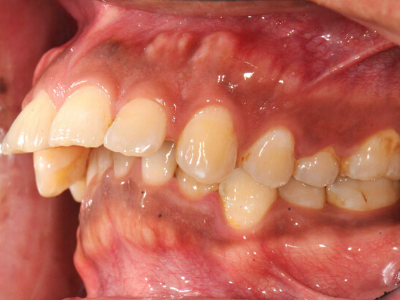
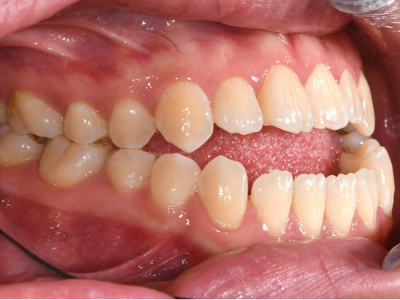
The upper and lower jaws can be thought of as the ‘foundation’ for the teeth and soft-tissues; braces can only straighten teeth and line up teeth, while surgery will allow for correction of jaw sizes and position to improve this ‘foundation’ for the teeth and soft tissues.
Benefits of such treatment include improvements in facial aesthetics and bite function.
When is surgery usually done?
Conventionally, surgery is done midway through during braces treatment. Before surgery, teeth are moved with braces to ensure that they fit well together after surgery, but it might feel like the bite is temporarily worse while this is being done.
Jaw surgery is done under general anaesthesia, and cuts are made in the mouth with minimal external scarring. The jaws are repositioned and held in their new positions with metal plates, screws and guiding elastic bands. Hospitalisation for 2-5 days after surgery is expected typically, while normal activities can resume about 3 weeks after surgery.
After surgery, braces treatment continues to ensure that the teeth fit well together. With improvements in digital diagnosis and treatment planning, suitable cases may also be able to undergo surgery before braces or early on in braces treatment.Surgery is also usually done only in non-growing patients as this provides a stable starting point for treatment because no further changes in jaw sizes are expected.
